Introduction
The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) represents a new approach to regional economic cooperation, emphasizing inclusive growth, sustainability, and resilience in the Indo-Pacific region. Recently, India and other member nations of IPEF celebrated the anticipated enforcement of key agreements like the Clean Economy Agreement and the Fair Economy Agreement, aiming to leverage this framework to deepen economic partnerships. India’s active participation in IPEF showcases its commitment to fostering economic stability, countering regional dominance, and advancing global cooperation.
What is the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)?
Background of IPEF
Launched in 2022 in Tokyo, Japan, the IPEF is a collaborative initiative among 14 countries: Australia, Brunei, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, and the United States. These nations together represent nearly 40% of the global GDP and 28% of global trade. The IPEF aims to promote robust economic engagement, secure trade relationships, and foster growth in one of the world’s most economically dynamic regions.
Key Pillars of IPEF
The IPEF is organized into four main pillars, each focusing on a specific area of economic cooperation:
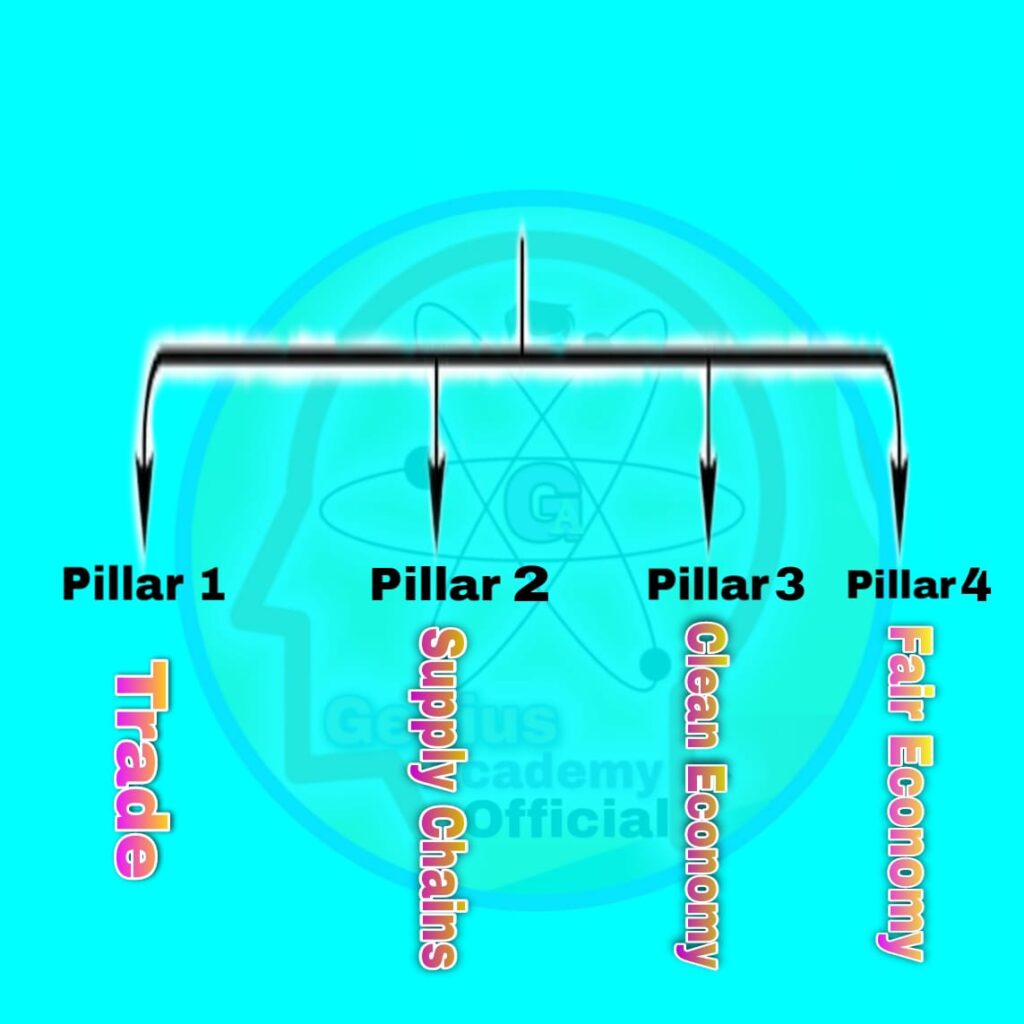
Trade (Pillar I):— This pillar focuses on reducing trade barriers and promoting inclusive, fair trading practices among member nations. By enhancing trade relations, the IPEF seeks to create a balanced trade environment and foster growth for all.
Supply Chains (Pillar II):— Recent global events have highlighted the need for resilient supply chains. This pillar aims to fortify supply networks, reducing dependence on any single source and ensuring continuous economic stability within the region.
Clean Economy (Pillar III):— With an emphasis on sustainable development, the Clean Economy pillar aligns with India’s focus on green energy, clean technology, and environmental conservation. By promoting clean energy initiatives and addressing climate change, this pillar contributes to the region’s transition to a greener economy.
Fair Economy (Pillar IV):— The Fair Economy pillar emphasizes the importance of fair economic practices, including anti-corruption initiatives and labor rights. It supports ethical business practices, transparency, and accountability.
Strategic Importance of IPEF
The IPEF holds significant strategic value as it seeks to promote cooperation among Indo-Pacific nations while countering regional challenges and supporting long-term prosperity.
1. Counterbalance to China’s Influence
One of the key motivations behind IPEF is to provide a strategic alternative to China’s growing economic dominance in the Indo-Pacific. By strengthening economic ties among member nations, the IPEF seeks to create a balanced and inclusive regional economy, countering China’s economic leverage in the region.
2. Strengthening Economic Ties
The IPEF enables member nations to deepen economic relationships and encourages collaboration across various sectors. This economic integration not only boosts trade but also fosters a sense of shared purpose, promoting stability in one of the world’s most economically vibrant regions.
3. An Alternative to Traditional Trade Blocs
Unlike conventional trade agreements, the IPEF operates as a non-traditional framework that provides a flexible alternative to trade blocs such as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). This approach allows member countries to participate without the rigid market access requirements typical of other trade pacts, making it more adaptable to diverse economic interests.
4. Addressing Critical Economic Challenges
Through agreements such as the Clean Economy Agreement and the Fair Economy Agreement, the IPEF directly addresses essential issues like sustainable growth, transparent governance, and fair trade practices. These agreements are designed to ensure that economic development in the region is inclusive, transparent, and conducive to long-term growth.
5. Facilitating Technological and Infrastructure Cooperation
The IPEF’s focus on sectors such as digital trade and clean energy opens avenues for technological transfer and infrastructure development. By encouraging cooperation in these fields, the framework supports sustainable growth and modern infrastructure improvements across the Indo-Pacific.
India’s Strategic Role within IPEF
India plays a significant role in IPEF, leveraging its economic strengths to contribute to and benefit from the framework’s initiatives.
1. Economic Integration and Trade Growth
India’s trade relationship with the U.S. has strengthened over the years, with merchandise exports increasing significantly. This rise in trade underscores the potential for further economic integration within the IPEF, creating new opportunities for India to enhance trade with other member countries.
2. Balancing Regional Influence
India’s participation in IPEF provides a counterbalance to China’s influence in the Indo-Pacific. By partnering with smaller economies in the region, India reassures these countries of its commitment to economic stability and security, offering an alternative to Chinese dominance.
3. Strengthening Supply Chain Resilience
India’s domestic initiatives, such as the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes and the Make in India program, align well with IPEF’s Supply Chain pillar. These initiatives enhance India’s manufacturing capabilities, contributing to resilient and diversified supply chains within the framework.
4. Leadership in Clean Energy and Sustainability
India has emerged as a global leader in renewable energy, particularly through initiatives like the International Solar Alliance (ISA). Its experience in clean energy positions India as a valuable contributor to IPEF’s Clean Economy pillar, aligning with both national and regional goals for a greener economy.
5. Promoting Digital and Technological Collaboration
With a rapidly growing digital economy and expertise in IT and digital services, India strengthens IPEF’s focus on digital and technological cooperation. India’s emphasis on Digital India, cybersecurity, and data governance enables it to take a leading role in developing secure and inclusive digital infrastructure in the Indo-Pacific region.
6. Building Strategic Alliances in the Indo-Pacific
IPEF aligns with India’s Act East Policy and enhances its relationships with ASEAN, the U.S., Japan, Australia, and other regional partners. By fostering these connections, India extends its influence in the Indo-Pacific, complementing other multilateral initiatives like the Quad and contributing to regional security and prosperity.
Key Challenges in Implementing IPEF
Despite its strategic benefits, the IPEF faces several challenges that may hinder its effectiveness.
1. Diverse Economic Interests among Members
With member countries at different stages of economic development and unique priorities, achieving consensus on common goals and standards can be challenging. This diversity may complicate negotiations and dilute the framework’s impact.
2. Absence of Market Access Commitments
Unlike traditional trade agreements, IPEF does not mandate market access commitments like tariff reductions, which could limit its appeal. Without such commitments, the framework may struggle to deepen economic ties in a meaningful way.
3. Political and Legislative Hurdles
In the U.S., the IPEF has raised concerns due to Congress’s authority over foreign commerce. Questions about the enforceability and durability of the agreements have emerged, potentially creating obstacles for consistent implementation.
4. Challenges in Enforcement and Compliance
IPEF’s reliance on voluntary compliance and cooperation rather than binding enforcement mechanisms may limit its effectiveness. This challenge is particularly relevant to the Clean Economy and Fair Economy agreements, where voluntary commitments may not guarantee compliance.
5. Issues of Data Localization and Privacy
Data localization, transparency, and fair competition are contentious issues that require global consensus. The lack of agreement on these matters could hinder IPEF’s ability to promote seamless digital trade and cooperation.
6. Geopolitical Tensions and Regional Pressure
Given its strategic aim to counterbalance China’s influence, IPEF could face geopolitical pressures that complicate negotiations. Countries may encounter external pressures, which could affect their commitment to the framework’s objectives.
Conclusion and Future Prospects
The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity offers a transformative opportunity for India to strengthen its regional presence and build sustainable economic partnerships. By participating in IPEF, India signals its commitment to an inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Indo-Pacific economy. Going forward, India’s proactive engagement in shaping the framework will be crucial to realizing its full potential, benefiting not only India but also promoting economic stability and shared prosperity across the region.
Source : – The Hindu

