GovAI: Reimagining Governance with Artificial Intelligence
Context
In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative technology capable of reshaping numerous aspects of society, particularly in governance. The potential for AI to revolutionize public administration and service delivery is especially significant in a rapidly digitalizing country like India. By integrating AI into governance structures—referred to as GovAI—India can enhance the efficiency, inclusivity, and responsiveness of public services. This initiative aligns with the broader global trend of harnessing AI’s potential for public good and holds immense promise for addressing complex societal challenges through data-driven decision-making.
AI Governance Overview
Definition:
AI governance refers to the policies, frameworks, and best practices designed to ensure the responsible and ethical development and use of AI technologies.
Purpose:—
- To minimize risks associated with AI systems.
- To maximize societal and economic benefits.
- To ensure AI technologies operate ethically and responsibly.
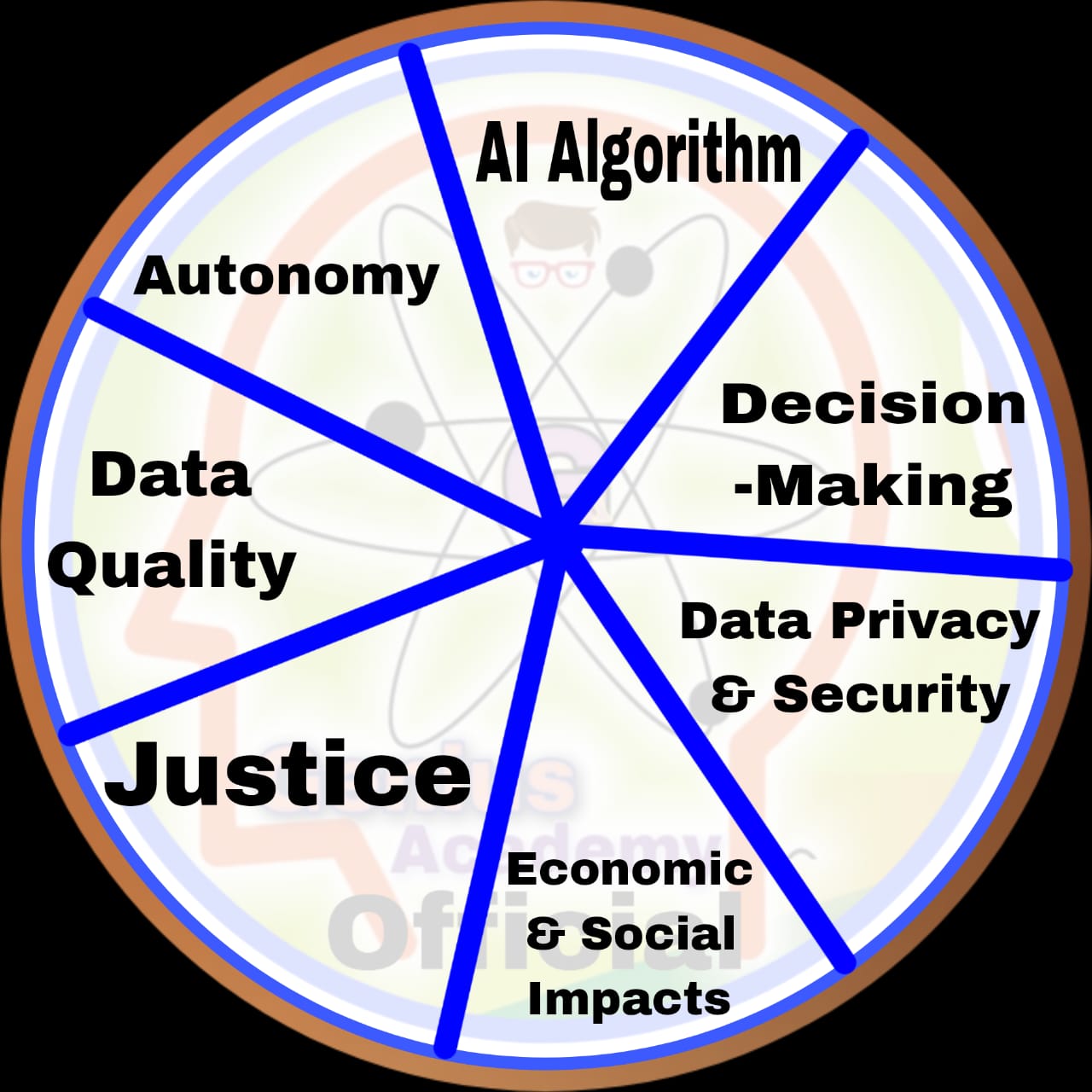
- AI Algorithms:— Ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI models.
- Decision-Making:— Mitigating biases and promoting just and fair automated decisions.
- Data Privacy and Security:— Protecting sensitive user data and ensuring secure data handling practices.
- Economic and Social Impacts:— Addressing AI’s implications on employment, inequality, and societal structures.
- Justice:— Supporting equal treatment and eliminating discriminatory AI outcomes.
- Data Quality:— Ensuring accuracy, completeness, and relevance of datasets used in AI systems.
- Autonomy:— Preserving human agency and control over AI-driven processes.
Digital Transformation of Governance in India
India has undergone a major digital transformation over the past decade. Efforts to develop a robust Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) have yielded substantial improvements in service delivery, reduced leakages in welfare schemes, and streamlined governance processes. The integration of digital tools has provided a strong foundation upon which AI-driven innovations can build, paving the way for GovAI to deliver even greater impact.
Revolutionizing Governance with AI
AI’s potential to revolutionize governance lies in its capacity to process vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, automate complex tasks, and derive actionable insights from seemingly chaotic datasets. As a catalyst for innovation across sectors, AI promises to streamline processes, optimize resource allocation, and offer personalized citizen services. For India, this represents a path toward more efficient, transparent, and inclusive governance.
Key Trends Driving GovAI
AI-driven governance in India is being shaped by several key trends and factors:
1. Rapid Digitalization
India has one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing internet user bases. With over 900 million internet users and projections suggesting that this number could reach 1.2 billion by 2026, the digital connectivity underpinning Indian society is immense. This connectivity supports the GovAI ecosystem by enabling real-time data collection, analysis, and dissemination for policy-making and public service delivery.
2. Data as a Resource
India’s digital ecosystem generates vast volumes of data, offering a unique opportunity to harness this resource for AI development. Programs like the IndiaDatasets Programme aim to create and utilize government datasets for AI innovation, all while adhering to data protection and privacy laws. Data-driven governance can lead to more precise policy interventions and optimized service delivery.
India’s Leadership in AI-Driven Governance
India has already demonstrated significant success in leveraging technology for governance, which positions it as a global leader in this space. The Global Partnership on AI (GPAI), chaired by India, emphasizes inclusive and trustworthy AI development for public good. By embracing GovAI, India can set an example for other nations, demonstrating the potential for technology to deliver effective, people-centric governance.
Potential Benefits of GovAI
The adoption of AI in governance can yield several important benefits:
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Service Delivery
AI-driven automation can streamline government operations, minimize manual intervention, and optimize resource allocation. AI-powered chatbots, for example, can provide 24/7 assistance to citizens, reducing waiting times, resolving queries quickly, and improving service delivery outcomes.
2. Data-Driven Decision Making
AI systems can process and analyze large datasets to identify trends, generate insights, and recommend targeted interventions. In sectors like healthcare, education, and social welfare, data-driven decision-making can lead to better policy outcomes, more effective resource allocation, and enhanced public welfare programs.
3. Increased Transparency and Accountability
AI can enhance transparency in government functions by automating and documenting processes, reducing opportunities for corruption, and ensuring efficient use of public resources. Automated decision-making systems can maintain detailed records of their operations, facilitating audits and accountability.
4. Proactive and Predictive Governance
AI can empower governments to adopt a proactive approach to public administration. Predictive analytics can be applied in disaster management to anticipate risks and prepare mitigation measures, in public health to monitor outbreaks, and in crime prevention to deploy law enforcement resources effectively.
Potential Drawbacks of GovAI
Despite its promise, integrating AI into governance comes with challenges and potential drawbacks:
1. Privacy Concerns
AI often relies on large-scale data collection and analysis, raising significant privacy concerns. Citizens may worry about their personal data being monitored, analyzed, or used without adequate consent. Maintaining a balance between data utility and individual privacy rights is crucial.
2. Accountability and Bias in AI Systems
AI systems are only as good as the data on which they are trained. Biased datasets can lead to discriminatory or inaccurate outcomes, undermining public trust. Determining accountability for AI-driven decisions is complex, particularly when errors occur. Clear regulatory mechanisms are needed to ensure accountability.
3. Risk of Increased State Control and Surveillance
The integration of AI in governance can potentially lead to greater state control and surveillance over citizens, raising concerns about individual freedoms and privacy. Safeguarding citizens’ rights while using AI for governance is a critical consideration.
4. Exacerbation of the Digital Divide
Not all citizens have equal access to digital technologies, and the benefits of AI-driven governance may not reach everyone. Those without the skills or means to engage with digital tools risk being marginalized, widening existing inequalities.
Way Forward: Overcoming Challenges to Realize the Potential of GovAI
To ensure that GovAI maximizes its potential while addressing key concerns, a comprehensive and balanced approach is required:
1. Implementing Robust Regulatory Frameworks
Clear laws and regulations should govern the collection, storage, and use of data in AI systems, with a focus on privacy, transparency, and accountability. Regulatory bodies must have the authority to monitor AI deployments, investigate violations, and protect citizens’ rights.
2. Promoting Ethical AI Development
AI systems must be designed with fairness, equity, and inclusivity as guiding principles. Bias audits, ethical testing, and comprehensive data validation procedures can help ensure AI outcomes are free from discrimination and harmful biases.
3. Enhancing Public Trust through Transparency
Transparent AI governance mechanisms, open-source models, and clear explanations of AI-driven decisions can foster public trust. Citizen engagement in policy-making, particularly on issues involving AI deployment, can further build confidence.
4. Strengthening Public Awareness and Digital Literacy
Public awareness campaigns and digital literacy initiatives are essential to ensure citizens understand AI’s capabilities, limitations, and potential risks. Empowering citizens with digital literacy can bridge the digital divide and foster informed participation.
5. Collaboration with Technology Partners
Collaborating with tech companies, academic institutions, and global partners can accelerate AI innovation and ensure its ethical deployment. Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) can facilitate knowledge sharing and resource mobilization for AI-driven projects.
6. Balancing State Power and Citizen Rights
While AI offers governments powerful tools for public administration, it is vital to uphold democratic values and safeguard individual freedoms. Strong oversight mechanisms and public accountability measures are necessary to prevent misuse.
Conclusion
GovAI has the potential to transform governance in India by enhancing efficiency, transparency, and responsiveness. By addressing privacy concerns, ensuring accountability, and mitigating potential negative impacts, India can harness AI’s potential to improve public administration and citizen welfare. With the right policies, frameworks, and ethical safeguards in place, GovAI can serve as a model for effective, citizen-centered governance in the AI era. This balanced approach can empower India to lead the world in harnessing AI for societal good, ensuring a future where technology serves humanity with fairness, inclusivity, and transparency.
Daily Mains Practice Questions
UPSC (CSE) Mains Questions from “GovAI: Reimagining Governance with AI”
General Studies Paper II – Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice, and International Relations
| [Q1.] Discuss the potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in transforming public administration in India. How can AI-driven governance enhance efficiency, transparency, and inclusivity in public services? |
| [Q2.] Examine India’s digital public infrastructure (DPI) and its significance in the evolution of AI-driven governance. What are the key challenges in leveraging this infrastructure for AI innovation in public services? |
| [Q3.] Analyze the impact of AI-driven decision-making on public policy. How can AI models improve data-driven governance while ensuring transparency and accountability? |
| [Q4.] Evaluate India’s role as a global leader in AI-driven governance through initiatives like the Global Partnership on AI (GPAI). How can India’s approach inspire other nations in leveraging AI for public good? |
| [Q5.] With the rapid expansion of AI technologies in governance, discuss the privacy and ethical concerns associated with large-scale data collection and surveillance. How can India balance AI-driven governance with individual rights and freedoms? |
General Studies Paper III – Technology, Economic Development, Bio-diversity, Environment, Security, and Disaster Management
| [Q6.] Critically assess the role of Artificial Intelligence in economic development and service delivery in India. How can AI help achieve economic inclusivity and efficiency in government operations? |
| [Q7.] What are the potential benefits and drawbacks of integrating AI into public administration, especially in terms of privacy concerns and state control? Suggest strategies to mitigate the challenges associated with AI-driven governance. |
| [Q8.] Discuss how predictive analytics and AI-based solutions can strengthen disaster management and public health monitoring in India. Provide examples of their potential impact. |
| [Q9.] Analyze the risks posed by biases in AI systems used for governance. How can India ensure ethical AI development to prevent discriminatory outcomes? |
| [Q10.] Examine the digital divide in India and its implications for AI-driven governance. How can public policy address these inequalities to ensure inclusive access to AI benefits? |
General Studies Paper IV – Ethics, Integrity, and Aptitude
| [Q11.] Discuss the ethical challenges posed by AI in governance. How can policymakers ensure that AI systems adhere to ethical principles like transparency, accountability, and non-discrimination? |
| [Q12.] The use of AI in governance presents potential risks of increased state surveillance and control. Discuss the ethical implications of such risks and propose measures to safeguard individual freedoms. |
| [Q13.] Evaluate the role of transparency, ethical standards, and citizen engagement in enhancing public trust in AI-driven governance. Why is public trust critical for the success of AI-based solutions in public services? |
| [Q14.] Explain how AI-driven decision-making can align with ethical governance practices. Provide examples of measures that can ensure AI systems respect human rights and dignity. |
FAQs on “GovAI: Reimagining Governance with AI”
1. What is GovAI?
Answer:—
GovAI refers to the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into public administration and governance. It aims to enhance efficiency, inclusivity, and responsiveness by streamlining processes, improving decision-making, and offering data-driven solutions to public issues.
2. How can AI enhance public service delivery in India?
Answer:—
AI can automate routine tasks, reduce bureaucratic delays, enable real-time service delivery (e.g., AI-powered chatbots), and provide personalized citizen services, leading to more efficient and accessible public administration.
3. What are the major benefits of AI-driven governance?
Answer:—
Key benefits include enhanced service efficiency, data-driven policy-making, increased transparency and accountability, proactive governance through predictive analytics, and optimized resource allocation.
4. What are the potential drawbacks of using AI in governance?
Answer:—
Drawbacks include privacy and data security concerns, potential biases in AI systems, the risk of increased state control and surveillance, and the potential to exacerbate the digital divide.
5. How can privacy concerns be addressed in AI-driven governance?
Answer:—
Implementing robust data protection laws, ensuring informed consent, promoting transparent AI systems, and having oversight mechanisms to monitor data use are key strategies to safeguard citizen privacy.
6. Why is data considered a critical resource for AI-driven governance?
Answer:—
Data serves as the foundation for developing AI models, which can analyze trends, optimize policies, and deliver targeted services. Initiatives like the IndiaDatasets Programme aim to harness government data for public good while ensuring data privacy.
7. What ethical challenges does AI pose in public administration?
Answer:—
Ethical challenges include potential biases in decision-making, accountability for AI-driven outcomes, transparency of AI operations, and the protection of citizen rights from potential state overreach.
8. What is the Global Partnership on AI (GPAI), and how is India involved?
Answer:—
The GPAI is an international initiative that promotes inclusive and trustworthy AI development. India’s leadership in GPAI reflects its commitment to leveraging AI for societal benefit and setting global standards in AI-driven governance.
9. How can AI help bridge the digital divide in India?
Answer:—
AI-driven solutions, if deployed equitably, can improve access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities for marginalized groups. However, addressing infrastructure gaps and enhancing digital literacy is critical.
10. What measures can India take to promote ethical AI development in governance?
Answer:—
Key measures include conducting bias audits of AI systems, promoting ethical AI frameworks, enhancing public awareness, ensuring regulatory oversight, and engaging with technology partners to develop fair AI solutions.





