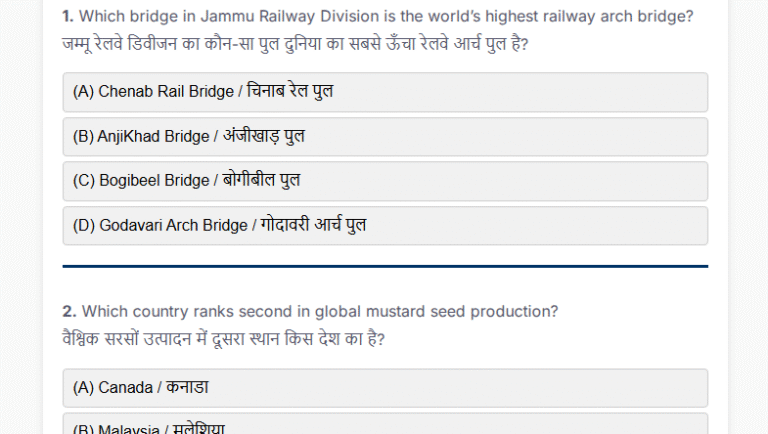
Current Affairs Today MCQs (13 Nov 2024)
1. What prompted Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu to consider pro-natalist policies?
(A) High fertility rates in the southern states
(B) Concerns over an ageing population
(C) TIncreasing population growth momentum
(D) Lack of healthcare facilities for the elderly
The correct answer is (B) Concerns over an ageing population
Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu are seeing significant growth in their elderly populations, which has sparked discussions on pro-natalist policies to counterbalance ageing demographics. The Southern states, including Kerala and Tamil Nadu, have lower fertility rates and higher life expectancy, leading to an older population. With the Total Fertility Rate (TFR) at 1.9 (below the replacement rate of 2.1), population growth in these regions is slower, and there is an increasing need to support elderly citizens while maintaining workforce levels.
2. By what year is India’s population expected to grow due to population momentum?
(A) 2050
(B) 2035
(C) 2070
(D) 2100
The correct answer is (C) 2070
India’s population growth is projected to continue until 2070 due to population momentum, even though the Total Fertility Rate (TFR) has dropped below the replacement rate. Population momentum occurs when a large proportion of the population is in the reproductive age group, resulting in continued population growth for several decades. While fertility rates are declining, this existing demographic structure will sustain population growth for years to come.
3. What percentage of Kerala’s population was elderly as of 2021?
(A) 10.1%
(B) 13.7%
(C) 16.5%
(D) 22.8%
The correct answer is (C) 16.5%
In 2021, 16.5% of Kerala’s population was elderly, highlighting its ageing demographic. Kerala has one of the highest proportions of elderly residents in India, reflecting the state’s high life expectancy and low fertility rates. By 2036, this percentage is projected to rise even further, reaching 22.8%, underscoring the growing need for policies to support the ageing population in the state.
4. What is the primary purpose of the Svalbard Global Seed Vault?
(A) To preserve biodiversity of Arctic species
(B) To safeguard global crop diversity as a backup
(C) To research agricultural advancements in cold climates
(D) To promote tourism in Norway’s Arctic region
The correct answer is (B) To safeguard global crop diversity as a backup
The Svalbard Global Seed Vault, located in Norway’s Arctic Svalbard archipelago, serves as a “doomsday” vault for safeguarding crop diversity. It holds over a million varieties of food crops as a backup for global gene banks, ensuring that seeds are preserved for emergencies and routine conservation. The vault’s natural freezing conditions provide a stable environment, helping to protect genetic diversity essential for global food security.
5. Which organization manages the Svalbard Global Seed Vault?
(A) United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
(B) Nordic Genetic Resources Centre
(C) World Health Organization (WHO)
(D) Green Climate Fund (GCF)
The correct answer is (B) Nordic Genetic Resources Centre
The Svalbard Global Seed Vault is managed by the Nordic Genetic Resources Centre under a U.N. treaty. This facility provides secure storage for seeds contributed by various gene banks worldwide, offering a no-cost backup for maintaining agricultural biodiversity. Only the original depositors can access their seeds, preserving ownership rights while ensuring that the seeds remain protected in a stable, long-term environment.
6. What environmental feature of Svalbard aids the natural preservation of seeds in the Global Seed Vault?
(A) Low rainfall
(B) Permafrost
(C) Volcanic soil
(D) Abundant vegetation
The correct answer is (B) Permafrost
Svalbard’s permafrost and low temperatures create an ideal environment for preserving seeds in the Global Seed Vault. The permafrost provides natural refrigeration, keeping the vault’s interior at -18°C and ensuring long-term stability even during power outages. This cost-effective, natural cooling system protects the seeds against extreme weather and climate threats, safeguarding global food security by preserving agricultural biodiversity.
7. What is the International Day for Preventing the Exploitation of the Environment in War & Armed Conflict focused on?
(A) Preventing pollution in industrial areas
(B) Highlighting environmental protection in conflict zones
(C) Promoting renewable energy usage globally
(D) Preserving marine biodiversity
The correct answer is (B) Highlighting environmental protection in conflict zones
The International Day for Preventing the Exploitation of the Environment in War & Armed Conflict, observed on November 6, focuses on protecting ecosystems in war-affected areas. This U.N.-initiated day raises awareness of the environmental consequences of armed conflict, emphasizing that preserving natural resources and ecosystems is as crucial as safeguarding human lives. It encourages global cooperation and adherence to laws, such as the Geneva Conventions, to minimize environmental damage during conflicts.
8. What does the International Day for Preventing the Exploitation of Environment in War & Armed Conflict advocate for?
(A) Strict trade regulations
(B) Strengthening legal protections for the environment in war
(C) Increased agricultural subsidies
(D) Enhanced urban development projects
The correct answer is (B) Strengthening legal protections for the environment in war
This international day, designated by the United Nations, calls for strengthening legal frameworks to protect the environment during armed conflicts. It advocates for enforcing international laws like the Geneva Conventions, which prohibit warfare tactics that cause severe environmental destruction. The day emphasizes that environmental stewardship is essential for sustainable peace and post-conflict recovery, encouraging efforts to protect ecosystems in conflict zones.
9. Which treaty grants depositors ownership rights over seeds stored in the Svalbard Global Seed Vault?
(A) Paris Agreement
(B) U.N. Biodiversity Treaty
(C) Geneva Convention
(D) U.N. Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture
The correct answer is (D) U.N. Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture
U.N. Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture
*Explanation:* The U.N. Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture governs the Svalbard Global Seed Vault, allowing depositors to retain ownership of their seeds. The vault acts as a secure backup, where only depositors can access their samples, preserving confidentiality and control. This system protects agricultural biodiversity, ensuring that gene banks worldwide have a resilient and accessible reserve of crop varieties for emergencies and conservation.
10. Why is India projected to continue growing in population despite a low Total Fertility Rate (TFR)?
(A) High fertility rates in all regions
(B) Population momentum from a large reproductive-age population
(C) Third generation
(D) Fourth generation
The correct answer is (B) Population momentum from a large reproductive-age population
Although India’s TFR has declined to 1.9, below the replacement rate of 2.1, the country’s population is expected to grow until 2070 due to population momentum. A substantial segment of the population remains in the reproductive age group, which will continue driving population growth even as fertility rates decrease. This momentum will sustain growth for several decades before stabilizing as the younger demographic ages.
11. How does permafrost in Svalbard contribute to the stability of the Global Seed Vault?
(A) It provides a source of natural light for seed growth
(B) It creates cost-effective natural refrigeration for seed storage
(C) It allows for water storage needed for the seeds
(D) It insulates seeds from harmful radiation
The correct answer is (B) It creates cost-effective natural refrigeration for seed storage
Svalbard’s permafrost helps maintain a stable, cost-effective refrigeration system for the seeds stored in the Global Seed Vault. Even in the event of power outages, the permafrost and low Arctic temperatures keep the vault’s interior cool at -18°C, preserving the seeds for long-term storage. This natural cooling system is crucial for protecting the genetic diversity of global food crops in case of global crises or climate threats.
12. What is the significance of the United Nations-backed global network supporting the Svalbard Global Seed Vault?
(A) It funds gene bank research across Europe only
(B) It promotes agricultural development in developed countries
(C) It enhances global food security and biodiversity
(D) It limits access to gene banks worldwide
The correct answer is (C) It enhances global food security and biodiversity
The United Nations-backed global network supporting the Svalbard Global Seed Vault plays a critical role in preserving food security and biodiversity by providing a secure, centralized backup for gene banks worldwide. Through contributions from various countries and organizations, this network helps protect crop varieties and genetic resources essential for resilient agriculture. In recognition of its importance, the vault was awarded the World Food Prize for its significant contributions to global food security.
13. What is the primary function of RNA editing in genetic treatments?
(A) Changing DNA sequences permanently
(B) Modifying RNA sequences after transcription
(C) Increasing protein production in cells
(D) Strengthening immune response against bacteria
The correct answer is (B) Modifying RNA sequences after transcription
RNA editing refers to the process of altering the sequence of RNA after it has been transcribed from DNA. By making changes to the mRNA, scientists can correct mistakes in the sequence, allowing the cell to produce accurate proteins. Unlike DNA editing, RNA editing is not permanent, and the edits may fade over time, requiring repeated treatments. This technology uses guide RNA (gRNA) to direct the enzyme ADAR to specific parts of the mRNA that need correction.
14. Which enzyme group is central to RNA editing and helps in the adenosine-to-inosine changes?
(A) Polymerase
(B) Ligase
(C) TADAR (Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA)
(D) Helicase
The correct answer is (C) ADAR (Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA)
ADAR enzymes are essential for RNA editing as they facilitate the conversion of adenosine (A) to inosine (I) within RNA sequences. This enzyme group is naturally present in the human body and allows scientists to make temporary changes in the mRNA, making the approach relatively safe with minimal immune reactions. ADAR-based editing is particularly useful because it enables specific, directed changes in RNA without permanently altering DNA, reducing the risk of irreversible errors.
15. Which of the following is a challenge specifically associated with RNA editing therapies?
(A) Permanent changes to genetic material
(B) Inability to accurately target the mRNA sequences
(C) Risk of allergic reactions due to bacterial proteins
(D) Transient nature requiring repeated treatments
The correct answer is (D) Transient nature requiring repeated treatments
RNA editing is temporary, meaning the edits to the RNA sequence do not last indefinitely. As a result, individuals undergoing RNA editing treatments may need repeated doses to sustain therapeutic effects. Unlike DNA editing, which results in permanent changes, RNA editing fades over time as the cell naturally degrades and replaces its mRNA, necessitating continued administration of the therapy to maintain results.
16. What is a unique trait of vampire bats’ social behavior?
(A) They form permanent social bonds and always groom each other
(B) They share food with bats that have previously helped them
(C) They prefer isolation and rarely interact with other bats
(D) They only socialize during mating seasons
The correct answer is (B) They share food with bats that have previously helped them
Vampire bats exhibit unique social behaviors, including food-sharing based on reciprocity. They remember which bats have shared food with them in the past and reciprocate accordingly, fostering cooperative relationships within their group. This behavior mirrors human social interactions, where new relationships start with small acts of sharing or mutual grooming before deeper bonds form. Such reciprocity helps vampire bats, which rely solely on a blood diet, to survive when food sources are scarce.
17. What adaptation allows vampire bats to locate feeding spots on their prey?
(A) Highly sensitive ears
(B) Specialized heat sensors in their snouts
(C) Echolocation abilities
(D) Enhanced sense of smell
The correct answer is (B) Specialized heat sensors in their snouts
Vampire bats have developed specialized heat sensors in their snouts, which help them identify the ideal feeding spots on their prey. These sensors detect warmth, guiding the bats to blood vessels close to the surface of the skin. This unique adaptation, combined with an anticoagulant in their saliva that keeps the blood flowing, makes vampire bats exceptionally efficient at feeding solely on blood.
18. Which organization lists the black-footed ferret as an endangered species?
(A) UNEP
(B) CITES Appendix III
(C) WWF
(D) IUCN
The correct answer is (D) IUCN
The black-footed ferret (Mustela nigripes), native to North America, is listed as “Endangered” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Conservation efforts are critical for this species, as it faces threats from habitat loss and diseases affecting its primary prey, the prairie dog. Successful cloning efforts are a significant step in supporting its population recovery.
19. Which method is used to deliver the gRNA-ADAR complex for RNA editing?
(A) Viral vectors
(B) Lipid nanoparticles
(C) Direct injection of ADAR enzymes
(D) Electroporation
The correct answer is (B) Lipid nanoparticles
Lipid nanoparticles are currently used to deliver the gRNA-ADAR complex for RNA editing. However, this delivery method has a limited carrying capacity, restricting its ability to transport large molecules effectively. Researchers continue to explore ways to improve delivery mechanisms to ensure that RNA editing therapies can be applied more efficiently and accurately, especially for complex genetic treatments.
20. How do perishable nature and risks of non-target effects challenge RNA editing?
(A) ADAR enzymes cause unintended adenosine-to-inosine changes
(B) The edits are permanent, increasing risk of mutations
(C) RNA editing uses proteins from bacteria, raising immune responses
(D) Editing needs to be redone, as effects diminish over time
The correct answer is (A) ADAR enzymes cause unintended adenosine-to-inosine changes
RNA editing via ADAR enzymes can sometimes result in off-target adenosine-to-inosine changes in unintended parts of the mRNA, or may miss targeted areas. This specificity challenge adds complexity to RNA editing, as scientists aim to develop methods that minimize non-target effects and increase precision. Additionally, since RNA editing is not permanent, effects fade over time, and repeated treatments are often necessary for sustained therapeutic impact.
_
Test Series of 1st Quarterly Current Affairs 2026 प्रथम त्रैमासिक करेंट अफेयर्स 2026 की टेस्ट सीरीज़…
Set 30 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 29 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 28 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 27 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 26 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 25 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 24 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 23 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 22 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 21 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 20 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 19 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 18 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 17 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 16 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 15 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 14 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 13 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 12 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 11 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 10 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 9 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 8 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 7 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 6 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 5 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 4 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 2 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 3 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…