Current Affairs Today MCQs (20 Nov 2024)
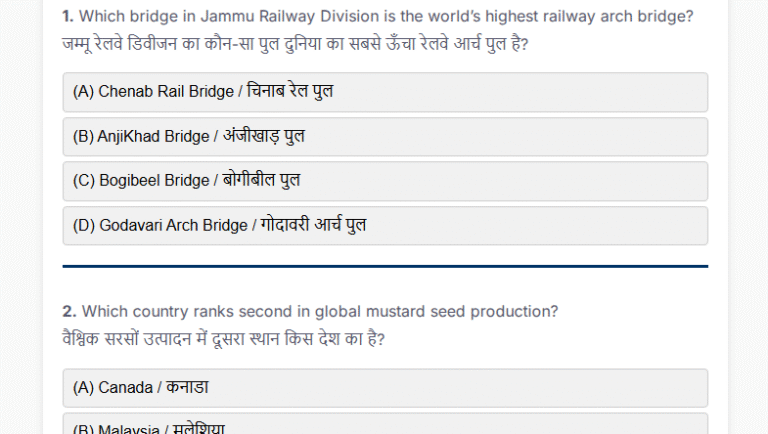
1. Who is eligible for the Ayushman Vay Vandana Card?
(A) Individuals below 60 years
(B) Only government employees
(C) Senior citizens aged 70 and above
(D) All citizens regardless of age
The correct answer is (C) Senior citizens aged 70 and above
The Ayushman Vay Vandana Card specifically targets senior citizens aged 70 and above, granting them free healthcare benefits under the Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY scheme.
2. How much health coverage is provided annually under the AB PM-JAY scheme?
(A) ₹2 lakhs per family
(B) ₹5 lakhs per family
(C) ₹10 lakhs per individual
(D) ₹1 lakh per individual
The correct answer is (B) ₹5 lakhs per family
The Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY scheme provides health coverage of ₹5 lakhs per family per year for secondary and tertiary care, making it the largest publicly funded health assurance program globally.
3. What is the funding ratio for Ayushman Bharat in northeastern states?
(A) ₹50:50
(B) 60:40
(C) 90:10
(D) 70:30
The correct answer is (C) 90:10
In northeastern and Himalayan states, the funding ratio for the Ayushman Bharat scheme is 90:10, with the central government contributing 90% of the funds.
4. Why is GSAT-20 being launched by SpaceX instead of India’s LVM-3 rocket?
(A) Higher efficiency of SpaceX rockets
(B) GSAT-20 is too heavy for LVM-3
(C) Lack of technological capabilities in India
(D) Reduced costs with SpaceX
The correct answer is (B) GSAT-20 is too heavy for LVM-3
Weighing 4,700 kg, GSAT-20 exceeds the payload capacity of India’s LVM-3 rocket, which can carry up to 4 tonnes to the geostationary transfer orbit. Hence, SpaceX’s Falcon-9 rocket will launch it.
5. What is the primary objective of NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)
(A) Conducting space research
(B) Manufacturing satellites
(C) Facilitating commercial exploitation of space products
(D) Training astronauts
The correct answer is (C) Facilitating commercial exploitation of space products
NSIL, ISRO’s commercial arm, focuses on promoting and commercially exploiting products and services derived from India’s space programs. It also supports high-tech industry participation in space activities.
6. What is the mission life of GSAT-20?
(A) 10 years
(B) 12 years
(C) 14 years
(D) 20 years
The correct answer is (C) 14 years
GSAT-20 has a mission life of 14 years, during which it will provide communication and internet services, particularly in remote and underserved areas of India.
7. Which population is most affected by sickle cell anemia in India?
(A) Tribal populations
(B) Urban populations
(C) Coastal communities
(D) Industrial workers
The correct answer is (A) Tribal populations
Sickle cell anemia is highly prevalent in tribal populations in India due to genetic factors and lack of access to healthcare. The commemorative stamp highlights efforts to address this issue, particularly in tribal regions.
8. Why is complete eradication of sickle cell anemia challenging?
(A) Lack of awareness
(B) Inadequate funding
(C) It is a genetic disorde
(D) Limited access to blood banks
The correct answer is (C) It is a genetic disorde
Sickle cell anemia is inherited, making it difficult to eliminate completely without breakthroughs in gene therapy or affordable stem cell transplants. Current treatments manage symptoms but do not eradicate the disease.
9. What does the sickle shape of RBCs in sickle cell anemia cause?
(A) Faster oxygen delivery
(B) Blockage in blood vessels
(C) Improved immunity
(D) Increased blood flow
The correct answer is (B) Blockage in blood vessels
The sickle-shaped RBCs become hard and sticky, leading to blockages in small blood vessels. This disrupts oxygen delivery to tissues and causes complications like pain and organ damage.
10. What is a unique feature of Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY?
(A) Age restriction for beneficiaries
(B) Limited hospital network
(C) No restriction on family size, age, or gender
(D) Coverage limited to primary care
The correct answer is (C) No restriction on family size, age, or gender
PM-JAY offers health coverage to all eligible families without restrictions on family size, age, or gender, ensuring comprehensive healthcare access for vulnerable populations.
11. What is the eligibility criterion for rural households under PM-JAY?
(A) Annual income above ₹5 lakhs
(B) Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) 2011 deprivation criteria
(C) Central Government employment
(D) Ownership of private health insurance
The correct answer is (B) Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) 2011 deprivation criteria
Eligibility for PM-JAY in rural areas is based on SECC 2011 deprivation criteria, targeting households with the greatest healthcare needs. Urban inclusion is based on occupational categories.
12. How does PM-JAY ensure cashless treatment for beneficiaries?
(A) Through empanelled hospitals
(B) By providing direct subsidies
(C) By offering insurance reimbursements
(D) Through pre-paid healthcare cards
The correct answer is (A) Through empanelled hospitals
Beneficiaries can access cashless treatment at empanelled public or private hospitals across India. This eliminates upfront costs, making healthcare accessible to economically weaker sections.
13. What is the key purpose of GSAT-20?
(A) Climate monitoring
(B) Navigation services
(C) High-speed internet connectivity
(D) Space exploration
The correct answer is (C) High-speed internet connectivity
GSAT-20 will enhance internet connectivity in remote and underserved areas of India, contributing to the country’s digital inclusion and communication infrastructure.
14. Why is NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) significant for India’s space program?
(A) It oversees all scientific missions
(B) It manages ISRO’s administrative tasks
(C) It replaces ISRO for satellite launches
(D) It commercializes India’s space products and services
The correct answer is (D) It commercializes India’s space products and services
NSIL focuses on promoting India’s space capabilities by facilitating industry participation and commercial exploitation of products and services developed through ISRO’s programs.
15. What distinguishes the Falcon-9 rocket in launching GSAT-20?
(A) Its low operational cost
(B) Its ability to launch from India
(C) Its payload capacity exceeding 4,700 kg
(D) Its ability to provide reusable technology
The correct answer is (C) Its payload capacity exceeding 4,700 kg
The Falcon-9 rocket is capable of carrying GSAT-20, which weighs 4,700 kg, exceeding the payload capacity of India’s LVM-3 rocket, making it suitable for this mission.
16. What is the main goal of the “Sickle Cell Eradication – 2047” initiative?
(A) Provide free healthcare to tribal populations
(B) Completely eradicate sickle cell anemia by 2047
(C) Promote gene therapy for genetic disorders
(D) Enhance research in blood-related disorders
The correct answer is (B) Completely eradicate sickle cell anemia by 2047
The initiative aligns with the long-term vision of eliminating sickle cell anemia, particularly in high-prevalence tribal regions. It emphasizes awareness, early detection, and advancing research for effective cures.
17. What is the primary cause of sickle cell anemia?
(A) Viral infection
(B) Poor diet
(C) Genetic mutation in the HBB gene
(D) Environmental factors
The correct answer is (C) Genetic mutation in the HBB gene
Sickle cell anemia is caused by a mutation in the HBB gene that leads to defective hemoglobin. This hereditary condition results in the formation of sickle-shaped red blood cells.
18. What is the major limitation of current treatments for sickle cell anemia?
(A) They are ineffective
(B) They are too costly and limited in availability
(C) They have severe side effects
(D) They cannot prevent genetic inheritance
The correct answer is (B) They are too costly and limited in availability
Current treatments like gene therapy and stem cell transplants are expensive and in developmental stages, making them inaccessible to a majority of affected populations.
19. What is the minimum age requirement for the Ayushman Vay Vandana Card?
(A) 50 years
(B) 60 years
(C) 70 years
(D) 75 years
The correct answer is (C) 70 years
The Ayushman Vay Vandana Card is specifically designed for senior citizens aged 70 and above, ensuring access to free healthcare services under PM-JAY.
20. Which beneficiaries are excluded from PM-JAY coverage under Ayushman Bharat?
(A) Private health insurance holders
(B) ESIC scheme beneficiaries
(C) CGHS beneficiaries
(D) Rural families
The correct answer is (C) CGHS beneficiaries
CGHS beneficiaries are required to choose between their existing scheme and PM-JAY, ensuring there is no duplication of healthcare benefits.
_
Test Series of 1st Quarterly Current Affairs 2026 प्रथम त्रैमासिक करेंट अफेयर्स 2026 की टेस्ट सीरीज़…
Set 30 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 29 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 28 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 27 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 26 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 25 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 24 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 23 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 22 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 21 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 20 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 19 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 18 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 17 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 16 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 15 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 14 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 13 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 12 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 11 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 10 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 9 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 8 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 7 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 6 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 5 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 4 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 2 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…
Set 3 Quarterly CA 2025 Jan to March IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS This test consists of 25 questions.At…